map的实现机制浅析
map数据结构
Golang的map使用哈希表作为底层实现,一个哈希表里可以有多个哈希表节点,也即bucket,而每个bucket就保存了map中的一个或一组键值对。
map数据结构由runtime/map.go:hmap定义:
type hmap struct {
count int // 当前保存的元素个数
...
B uint8
...
buckets unsafe.Pointer // bucket数组指针,数组的大小为2^B
...
}下图展示一个拥有4个bucket的map:
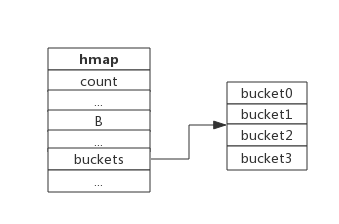
本例中, hmap.B=2, 而hmap.buckets长度是2^B为4. 元素经过哈希运算后会落到某个bucket中进行存储。查找过程类似。
bucket很多时候被翻译为桶,所谓的哈希桶实际上就是bucket。
bucket数据结构
bucket数据结构由runtime/map.go:bmap定义:
type bmap struct {
tophash [8]uint8 //存储哈希值的高8位
data byte[1] //key value数据:key/key/key/.../value/value/value...
overflow *bmap //溢出bucket的地址
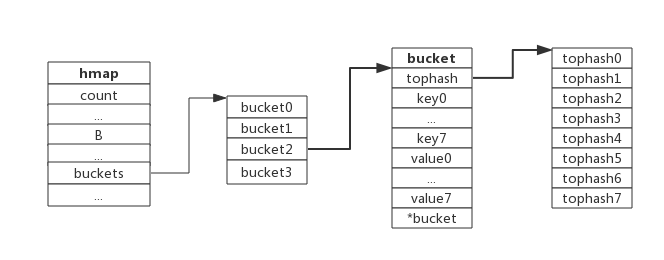
}每个bucket可以存储8个键值对。
- tophash是个长度为8的数组,哈希值相同的键(准确的说是哈希值低位相同的键)存入当前bucket时会将哈希值的高位存储在该数组中,以方便后续匹配。
- data区存放的是key-value数据,存放顺序是key/key/key/…value/value/value,如此存放是为了节省字节对齐带来的空间浪费。
- overflow 指针指向的是下一个bucket,据此将所有冲突的键连接起来。
注意:上述中data和overflow并不是在结构体中显示定义的,而是直接通过指针运算进行访问的。
下图展示bucket存放8个key-value对:
查找过程
查找过程如下:
- 根据key值算出哈希值
- 取哈希值低位与hmap.B取模确定bucket位置
- 取哈希值高位在tophash数组中查询
- 如果tophash[i]中存储值与哈希值相等,则去找到该bucket中的key值进行比较
- 当前bucket没有找到,则继续从下个overflow的bucket中查找。
- 如果当前处于搬迁过程,则优先从oldbuckets查找
注:如果查找不到,也不会返回空值,而是返回相应类型的0值。
插入过程
新元素插入过程如下:
- 根据key值算出哈希值
- 取哈希值低位与hmap.B取模确定bucket位置
- 查找该key是否已经存在,如果存在则直接更新值
- 如果没找到将key,将key插入
删除元素
delete() 函数用于删除集合的元素, 参数为 map 和其对应的 key。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
/* 创建map */
countryCapitalMap := map[string]string{"France": "Paris", "Italy": "Rome", "Japan": "Tokyo", "India": "New delhi"}
fmt.Println("原始地图")
/* 打印地图 */
for country := range countryCapitalMap {
fmt.Println(country, "首都是", countryCapitalMap [ country ])
}
/*删除元素*/ delete(countryCapitalMap, "France")
fmt.Println("法国条目被删除")
fmt.Println("删除元素后地图")
/*打印地图*/
for country := range countryCapitalMap {
fmt.Println(country, "首都是", countryCapitalMap [ country ])
}
}hashmap简单实现
基于 go 实现简单 HashMap,暂未做 key 值的校验。
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type HashMap struct {
key string
value string
hashCode int
next *HashMap
}
var table [16](*HashMap)
func initTable() {
for i := range table{
table[i] = &HashMap{"","",i,nil}
}
}
func getInstance() [16](*HashMap){
if(table[0] == nil){
initTable()
}
return table
}
func genHashCode(k string) int{
if len(k) == 0{
return 0
}
var hashCode int = 0
var lastIndex int = len(k) - 1
for i := range k {
if i == lastIndex {
hashCode += int(k[i])
break
}
hashCode += (hashCode + int(k[i]))*31
}
return hashCode
}
func indexTable(hashCode int) int{
return hashCode%16
}
func indexNode(hashCode int) int {
return hashCode>>4
}
func put(k string, v string) string {
var hashCode = genHashCode(k)
var thisNode = HashMap{k,v,hashCode,nil}
var tableIndex = indexTable(hashCode)
var nodeIndex = indexNode(hashCode)
var headPtr [16](*HashMap) = getInstance()
var headNode = headPtr[tableIndex]
if (*headNode).key == "" {
*headNode = thisNode
return ""
}
var lastNode *HashMap = headNode
var nextNode *HashMap = (*headNode).next
for nextNode != nil && (indexNode((*nextNode).hashCode) < nodeIndex){
lastNode = nextNode
nextNode = (*nextNode).next
}
if (*lastNode).hashCode == thisNode.hashCode {
var oldValue string = lastNode.value
lastNode.value = thisNode.value
return oldValue
}
if lastNode.hashCode < thisNode.hashCode {
lastNode.next = &thisNode
}
if nextNode != nil {
thisNode.next = nextNode
}
return ""
}
func get(k string) string {
var hashCode = genHashCode(k)
var tableIndex = indexTable(hashCode)
var headPtr [16](*HashMap) = getInstance()
var node *HashMap = headPtr[tableIndex]
if (*node).key == k{
return (*node).value
}
for (*node).next != nil {
if k == (*node).key {
return (*node).value
}
node = (*node).next
}
return ""
}
//examples
func main() {
getInstance()
put("a","a_put")
put("b","b_put")
fmt.Println(get("a"))
fmt.Println(get("b"))
put("p","p_put")
fmt.Println(get("p"))
}
